Understanding Life Insurance: Types, Benefits, and Considerations
Life insurance is a financial product designed to provide a payout to beneficiaries in the event of the insured individual’s death. It offers financial protection and peace of mind to policyholders and their loved ones. Here’s an overview of life insurance, including its types, benefits, and considerations: Types of Life Insurance: Term Life Insurance: Provides coverage for a specified term, such as 10, 20, or 30 years. Pays out a death benefit to beneficiaries if the insured dies during the term. Typically more affordable than permanent life insurance. Whole
Life Insurance: Offers coverage for the entire life of the insured, as long as premiums are paid. Includes a cash value component that grows over time. Premiums are generally higher compared to term life insurance. Universal Life Insurance: Combines a death benefit with a savings component. Provides flexibility in premium payments and death benefits. Cash value earns interest based on market performance or a minimum guaranteed rate. Variable Life Insurance: Allows policyholders to allocate premiums into investment accounts. Cash value and death benefit may fluctuate based on the performance of underlying investments. Offers potential for higher returns but also carries
investment risk. Benefits of Life Insurance: Financial Protection: Life insurance provides a lump-sum payment to beneficiaries, helping them cover living expenses, debts, and future financial needs after the insured’s death. Estate Planning: Proceeds from life insurance can be used to pay estate taxes, ensuring assets are preserved for heirs. Income Replacement: The death benefit can replace lost income, ensuring beneficiaries maintain their standard of living. Debt Repayment: Life insurance can be used to settle outstanding debts, such as mortgages, loans, or credit card balances, preventing financial burden on survivors. Business Continuation: Business owners can use life
insurance to fund buy-sell agreements, ensuring smooth transition of ownership in the event of a partner’s death. Considerations: Coverage Amount: Determine the appropriate coverage amount based on financial obligations, future expenses, and income replacement needs. Premiums: Understand the cost of premiums and ensure they fit within your budget. Underwriting: Insurers evaluate factors such as age, health, lifestyle, and occupation to determine eligibility and premium rates. Policy Riders: Consider adding riders for additional coverage, such as
accelerated death benefit, accidental death benefit, or waiver of premium. Review and Update: Regularly review your life insurance needs to ensure coverage remains adequate, especially after major life events like marriage, birth of a child, or purchase of a home. Comparison Shopping: Obtain quotes from multiple insurers to find the most competitive rates and suitable coverage options. Tax Implications: Consult with a tax advisor to understand the tax implications of life insurance, including income tax on withdrawals or estate taxes on large policies. Life insurance
plays a crucial role in financial planning, providing protection and security for individuals and their families. It’s essential to choose the right type and coverage amount based on individual needs and circumstances. Consulting with a financial advisor can help navigate the complexities of life insurance and make informed decisions.Let’s delve deeper into the considerations when choosing a life insurance policy: 1. Coverage Amount: Needs Assessment: Conduct a thorough evaluation of your financial obligations, including debts, mortgages, education expenses, and ongoing living expenses. Income Replacement: Determine the amount needed to replace lost income and sustain
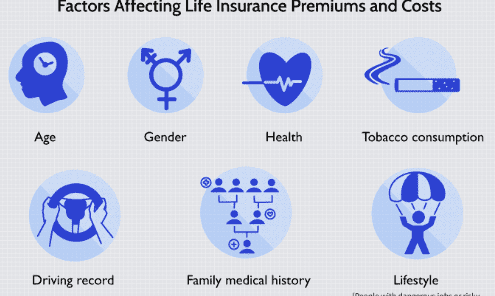
your family’s standard of living in your absence. Future Needs: Anticipate future financial needs such as retirement savings, college funds for children, and healthcare expenses. 2. Premiums: Affordability: Assess your budget to ensure you can comfortably afford the premiums throughout the policy term. Premium Structure: Understand whether premiums are fixed (as in term insurance) or may vary based on market performance or policy adjustments (as in universal or variable life insurance). Payment Frequency: Choose a premium payment schedule that aligns with your cash flow, whether it’s monthly, quarterly, semi-annually, or annually. 3. Underwriting: Health
Assessment: Be prepared for the insurer to evaluate your health status through medical exams, questionnaires, and medical history reviews. Risk Factors: Understand how factors such as age, health conditions, lifestyle choices (like smoking or hazardous occupations), and family medical history can affect premiums and insurability. Preferred Rates: Some insurers offer preferred rates for individuals with excellent health and lifestyle habits, potentially reducing premium costs. 4. Policy Riders: Additional Coverage: Consider adding riders to customize your policy based on specific needs, such as: Accelerated Death Benefit: Allows access to a portion of the death benefit if diagnosed with a terminal illness. Waiver of Premium: Waives premium payments if you become disabled and
unable to work. Child Term Rider: Provides coverage for children under the policy. Costs: Evaluate the cost-effectiveness of each rider and whether the benefits they provide align with your needs. 5. Review and Update: Life Changes: Regularly reassess your life insurance needs following major life events like marriage, divorce, birth of a child, or significant changes in income or assets. Policy Review: Review your policy annually to ensure it still meets your needs and consider adjustments if necessary. Beneficiary Designations: Keep beneficiary designations up to date, reflecting changes in relationships or circumstances. 6. Comparison Shopping: Multiple Quotes: Obtain quotes from multiple insurers to compare coverage options, premium rates, and policy features. Financial Strength:
Research insurers’ financial stability and ratings to ensure they can fulfill their obligations in the long term. Customer Service: Consider the quality of customer service, claims process efficiency, and policyholder satisfaction when selecting an insurer. 7. Tax Implications: Death Benefit Taxation: Life insurance death benefits are generally income tax-free for beneficiaries. Estate Taxes: Depending on the size of the policy and the value of your estate, life insurance proceeds could be subject to estate taxes. Consider estate planning strategies to minimize tax liabilities. Cash Value Accumulation: Understand the tax treatment of cash value accumulation and withdrawals in permanent
life insurance policies, which may have tax implications. By carefully considering these factors, you can make informed decisions when choosing a life insurance policy that provides adequate coverage and financial protection for you and your loved ones. Consulting with a financial advisor or insurance professional can offer valuable guidance tailored to your individual circumstances.